Purine and Pyrimidine Metabolism
Purines include adenine, guanine, hypoxanthine, xanthine, and uric acid
Pyrimidines include cytosine, uracil, thymidine (5-methyl uracil), and orotic acid
Þ T is only non-SAM methylation (uses methylene from N5,N10-CH2-THF)-hence methotrexate good to stop cell division
Ribose-5-phosphate (from pentose pathway) reacted with ATPÞ AMP
- produces 5-phosphoribosyl-1-pyrophosphate (PRPP)
- catalyzed by ribose phosphate pyrophosphokinase
- regulation: Pi(+) nucleotide breakdown; ADP/GDP(-) dont need
- bases are added to C-1; nucleosides (without C-5 PO3) from breakdown of NTs
Pyrimidine Synthesis
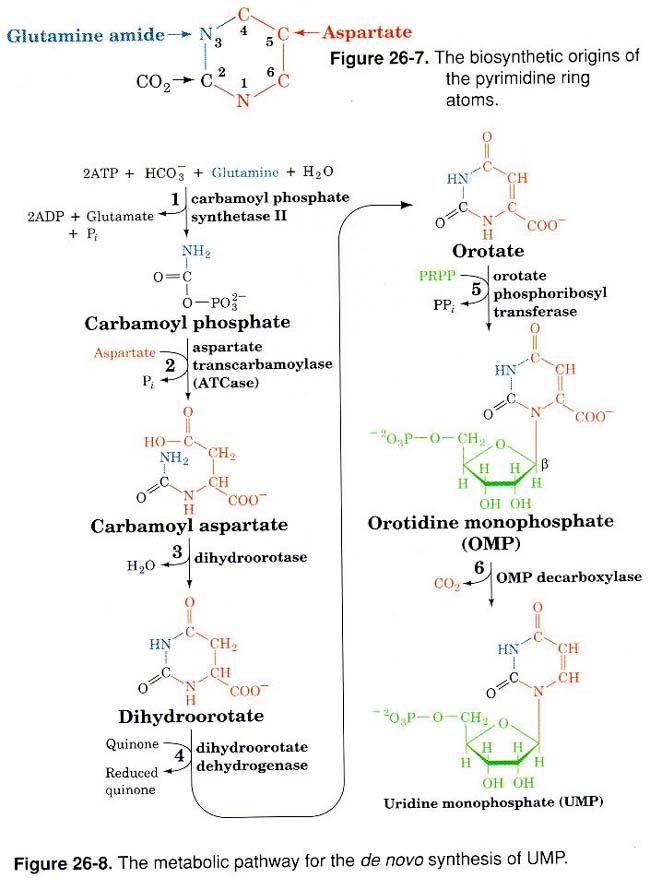
- Orotate
is the first pyrimidine; OMP is first nucleotide
- Purine synthesis begins with carbamoyl phosphate synthase (CPS II)
- similar to urea cycle CPS I, except in cytoplasm not mitochondira and less active
- CAD protein
performs first three reactions
- (CPS II, aspartate transcarbamoylase, dihydroorotase)
- major regulated step UTP(-)
feedback control
- One enzyme condenses orotic acid with PRPP and decarboxylates orotidine-5P
- if deficient: orotic aciduria lethal if untreated homozygote no pyrimidines
- also excess PRPP, so sugar fermentation and overproducion of purines
- Nucleoside diphosphokinase
add pyrimidine to PRPP
- increased in metastatic cancer
Purine Synthesis
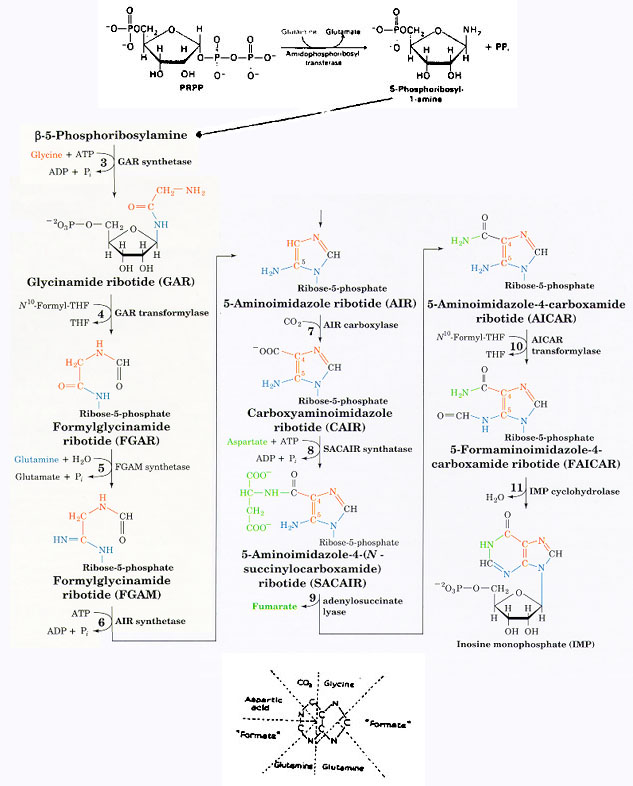
- Hypoxanthine
is the first purine; IMP is the first nucleotide
- Unlike pyrimidines, purines are manufactured directly on the PRPP
- begins with PRPP + glutamate Þ phosphoribosylamine (PRA)
- Amidophosphoribosyl transferase
primary regulated step
- PRPP(+)
substrate availability; AXP/GXP(-) feedback
- Synthesis of 5-membered ring first, then 6-membered ring
- THF donates 2 formyl groups in the process
- IMP Þ GMP or AMP presence of GTP or ATP initiates producion of the other
- salvage pathway
add purine to PRPP
- adenine
or hypoxanthine/guanine phosphoribosyl transferase (APRT/HGPRT)
- Lesch-Nyham Syndrome
deficiency in HGPRT self-mutilation
Fate of Nucleotides
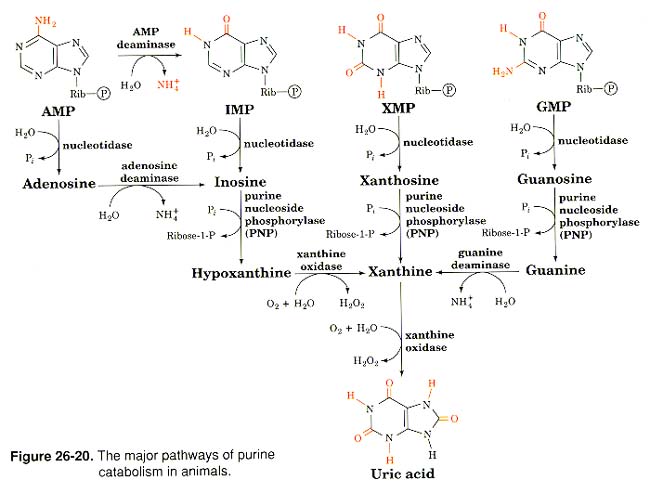
- (1) Use in RNA, ATP, etc.
- (2) Formation of deoxynucleotides
enzyme: ribonucleotide reductase; two regulatory regions:
- (1) overall activity - dATP(-)
- (2) specific activity binding of purine or pyrimidine makes other
- (3) Degradation
- base oxidized to uric acid (too much uric acid Þ Gout, joint pain)
- allopurinol
inhibits xanthine oxidase hypoxanthine is more soluble
- adenosine deaminase deficiency Þ SCID (severe combined immunodefic.)
Inhibition of Nucleotide Synthesis
- (1) Folic acid analog (methotrexate) stop methylation (dTMP formation)
- (2) hypoxanthine analogs (6-mercaptopurine and azathioprine)
- react with PRPP to form nucleotides inhibit synthesis of PRA, AMP, GMP
- used for organ transplantation
(3) 5-fluorouracil reacts with PRPP to form dUMP analogue
- irreversably inavtivates thymidylate synthase similar to methotrexate



