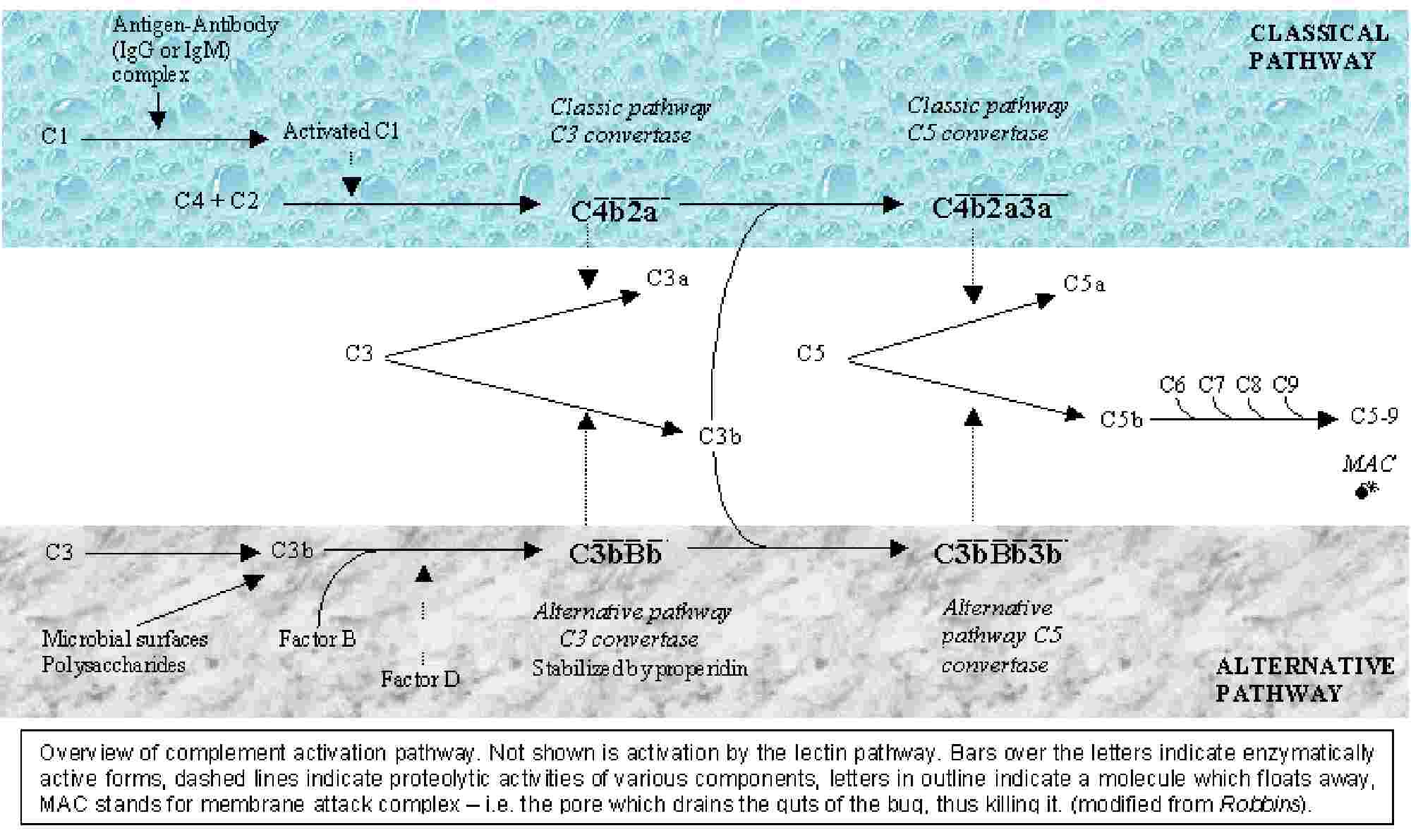
The Complement System
Introduction
Terminology
:|
1. PATHWAYS: |
Classical, Alternative, Terminal |
|
2. PROTEINS : |
Classical/Terminal Components: C1, C4, C2, C3, C5, C6, C7, C8, C9 |
|
3. ACTIVATED PROTEIN (i.e. enzyme) |
Anything that has a bar over it is an enzyme (not shown here) |
|
4. ACTIVATION PRODUCTS: |
Lower case letters indicate the fragments status, a = released, b = bound. Examples: C3b, C5a, Bb. EXCEPTION: C2 C2a is bound form, C2b is released form |
|
5. UPPER CASE |
An upper case letter after a component indicates it is a factor, inhibitor, or gene product. Examples: C4A and C4B are gene products. |
Overview

Classical Pathway
Alternative Pathway
Terminal Pathway
Complement Activation
serves three functions in inflammation:Complement Activation Pathways and Regulation
Pathological States
C3 Receptors Extrinsic Regulation
regulates complement on target cells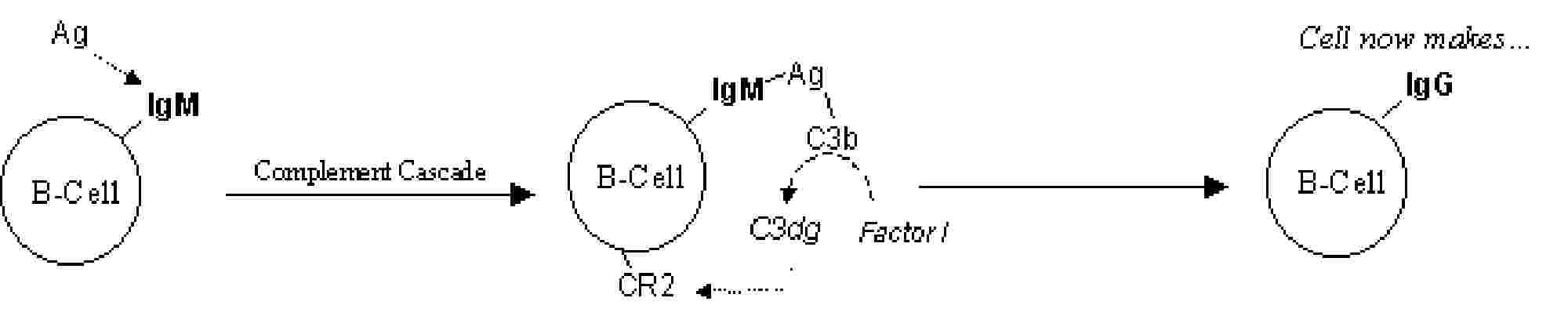
Complement Genes
Measurement of Complement
Complement and Disease