Basal Ganglia
Definition and Terminology
Topography
Components of the Basal Ganglia
putamen but excitatory to the substantia nigra
|
Component |
Neurotrans |
Afferent |
Efferent |
|
cortex |
glutamate |
- |
caudate and putamen |
|
striatum (caudate+putamen) |
GABA, ACh, somatostatin |
cortex |
GPe, substantia nigra |
|
ext. globus pallidus (GPe) |
GABA |
striatum |
subthalamic nucleus via subthalamic fasciculus and GPi |
|
int. globus pallidus (GPi) |
GABA |
GPe and subthalamic nucleus |
thalamus |
|
subthalamic nucleus |
glutamate |
GPe,motor and premotor cortices |
GPi and GPe |
|
substantia nigra – compact part (pars compacta, pigmented) |
dopamine |
- |
lat. caudate nucleus and putamen; this dopamine modulates output of globus pallidus |
|
substantia nigra – reticular part (pars reticulata,unpigmented) |
GABA |
striatum and subthalamic nuclei |
medial caudate nucleus, putamen, VL/VA nucleus of thalamus |
|
thalamus |
glutamate |
GPi and reticular part of subst.nigra |
cortex |
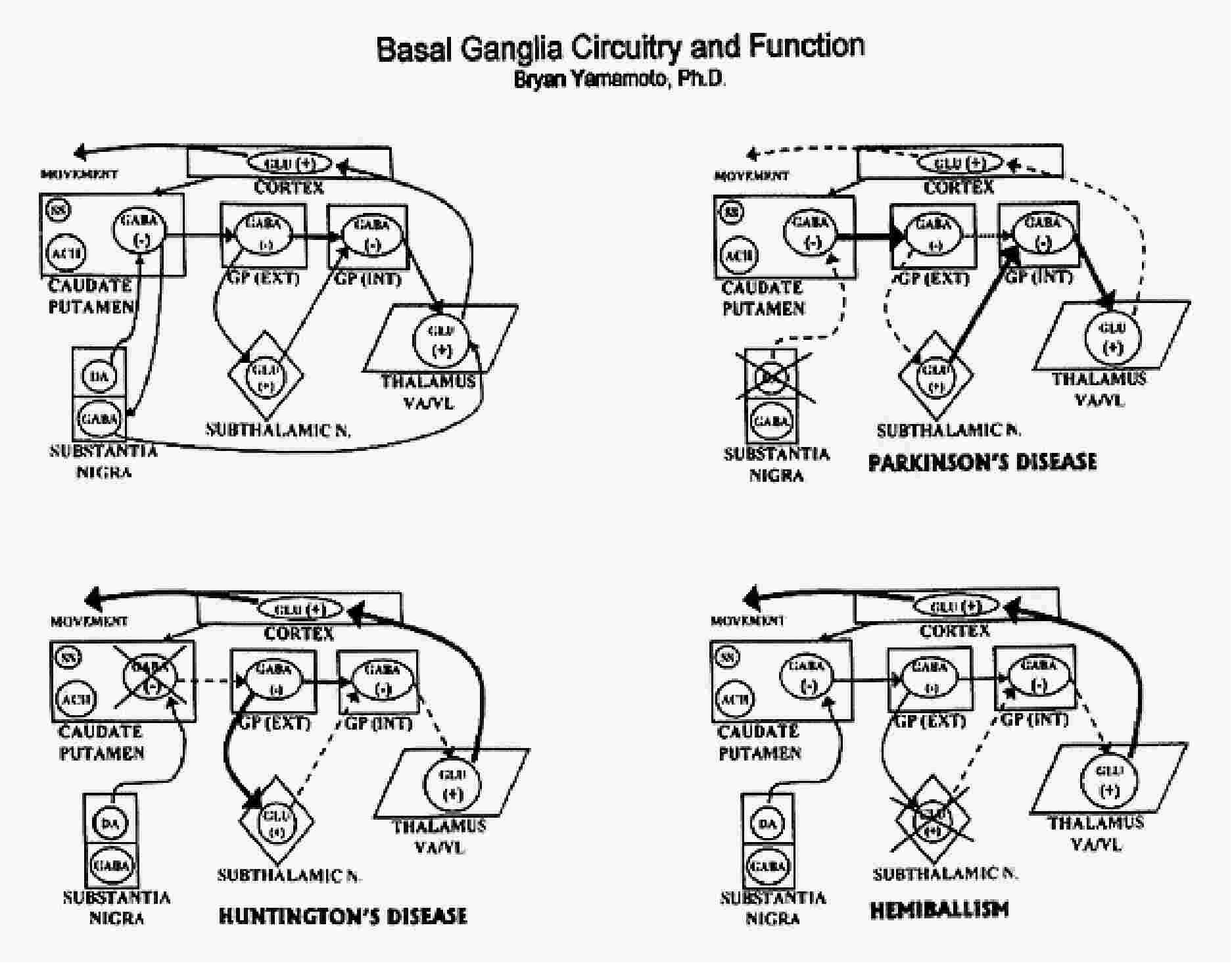
Connections of the Basal Ganglia
– see figure belowPathology of the Basal Ganglia
– see figure below
Cerebellum Vs. Basal Ganglia
|
Basal Ganglia |
Cerebellum |
|
Receives input from all areas of cortex |
Input primarily from sensory motor region |
|
No sensory input |
Receives sensory input |
|
No projections to brainstem and vestibular nuclei |
Projections to brainstem and vestibular nuclei |
|
Initiation of movement |
Modulation of movement |
|
Lesion: tremor, rigidity, and chorea |
Lesion: ataxia |